
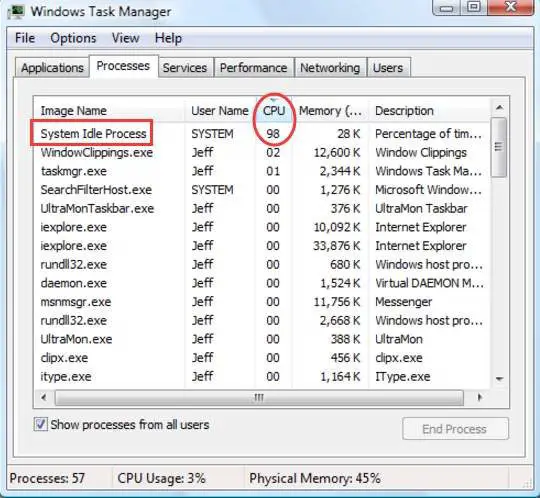
Choose High for 2 updates per second, Normal for 1 update per second, and Low for an update every 4 seconds.
Update speed - sets the rate at which resource data is updated throughout Task Manager. Refresh now - when tapped or clicked, instantly update all of the regularly updated hardware resource data found throughout Task Manager. Show history for all processes - if selected, shows data for non-Windows Store apps and programs in the App History tab.  Show full account name - if selected, displays a user's real name next to the user's username where applicable. Set default tab - sets which tab Task Manager opens to each time it's first launched. It will, in either case, always appear in the taskbar notification area (the space next to the clock with the little icons). Hide when minimized - if selected, will prevent Task Manager from showing up in the taskbar like a normal program. Minimize on use - if selected, will minimize Task Manager when you choose the Switch to option, available in several areas throughout the tool. Always on top - if selected, will keep Task Manager in the foreground at all times. It will not end any apps, programs, or processes you're viewing or have selected. Exit - will close the Task Manager program. You also have the option to Create this task with administrative privileges, which will run the executable with "elevated" permissions. From here you can browse to, or enter the path of, any executable on your computer and open it. Run new task - opens the Create new task dialog box. Right now, however, let's look at your menu options and what features and choices you have access to there: There's a mind-boggling level of information available in Task Manager about what's going on in Windows, from overall resource usage down to minute details like how many seconds each individual process has used of the CPU's time.Įvery little bit, tab by tab, is fully explained in this enormous document.
Show full account name - if selected, displays a user's real name next to the user's username where applicable. Set default tab - sets which tab Task Manager opens to each time it's first launched. It will, in either case, always appear in the taskbar notification area (the space next to the clock with the little icons). Hide when minimized - if selected, will prevent Task Manager from showing up in the taskbar like a normal program. Minimize on use - if selected, will minimize Task Manager when you choose the Switch to option, available in several areas throughout the tool. Always on top - if selected, will keep Task Manager in the foreground at all times. It will not end any apps, programs, or processes you're viewing or have selected. Exit - will close the Task Manager program. You also have the option to Create this task with administrative privileges, which will run the executable with "elevated" permissions. From here you can browse to, or enter the path of, any executable on your computer and open it. Run new task - opens the Create new task dialog box. Right now, however, let's look at your menu options and what features and choices you have access to there: There's a mind-boggling level of information available in Task Manager about what's going on in Windows, from overall resource usage down to minute details like how many seconds each individual process has used of the CPU's time.Įvery little bit, tab by tab, is fully explained in this enormous document.








